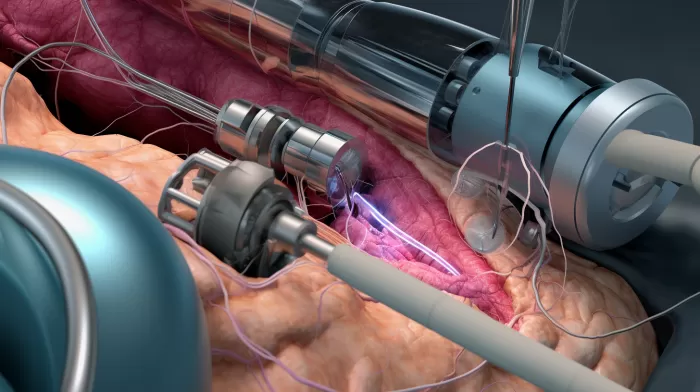
When it comes to undergoing a hysterectomy, there’s one method that may pose a significant risk to your health that you need to know about. It’s called minimally invasive power morcellation, and new research published in the Journal of the American Medical Association reveals a chilling possibility: this particular hysterectomy procedure might actually spread undetected cancer.
What is Minimally Invasive Power Morcellation?
During a minimally invasive power morcellation hysterectomy, surgeons use a medical device called a morcellator to break down uterine tissue into small fragments. These fragments are then removed through tiny incisions in the abdomen via a tube or laparoscope. The procedure has been lauded for its ability to significantly reduce recovery time and post-operative scarring due to its minimally invasive nature.
But here’s the catch – when a morcellator breaks up the uterus, it might also break undetected cancer cells and cause them to enter the bloodstream, allowing them to spread to other areas of the body. This is a risk that is not present with conventional hysterectomies, where the uterus is removed in one piece without being fragmented.
The concept is chilling and raises tough questions about the safety and ethics of this popular procedure. But, before making any concrete decisions, let’s examine the facts and figures.
Prevalence of Hysterectomies
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, hysterectomies are the second most common surgery undergone by women in the United States. The procedure is carried out for various reasons, including cancer, fibroids, endometriosis, and chronic pelvic pain.
In total, it is estimated that around 600,000 hysterectomies are performed each year in the U.S., and the morcellation procedure accounts for about 20% of them. That means roughly 120,000 women could potentially be at risk for cancer cell spreading if it is present.
Research Findings on Morcellation Hysterectomies
The researchers conducted an extensive review of the clinical data and found that the risk of cancer spreading through morcellation turned out to be higher than initially thought. In fact, the procedure increased the chances of a woman developing an aggressive form of uterine cancer known as leiomyosarcoma.
Furthermore, the researchers discovered that cancer cells could be present even in ‘low-risk’ patients. These findings were shocking and had the potential to spur dramatic changes in the way hysterectomies are done in the future.
Alternatives to Minimally Invasive Power Morcellation
Given the risks associated with morcellation hysterectomies, other methods may be better suited for certain individuals. It’s important to remember that each patient has a unique medical history and situation, which should be carefully considered before making a decision.
One alternative to morcellation is a conventional hysterectomy, where the uterus is removed in one piece. This procedure eliminates the risk of cancer spread by morcellation. Another option is a laparoscopic hysterectomy without morcellation, which can offer similar benefits to minimally invasive surgery without the risks associated with morcellation.
The FDA’s Stance on Morcellation
In light of the risks associated with power morcellation, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has issued an updated safety communication recommending that healthcare providers not use laparoscopic power morcellation for treating uterine fibroids. The FDA advises individuals to discuss various treatment options with their healthcare providers before opting for morcellation procedures.
Informed Decision-Making for Your Health
The most important thing to take away from this information is the importance of making informed decisions when it comes to your health. If you’re scheduled to undergo a hysterectomy, it’s crucial that you discuss all available options with your healthcare provider, keeping in mind the risks and benefits associated with morcellation procedures.
By staying vigilant and seeking out the knowledge you need to make well-informed decisions, you can minimize your risks and take critical steps towards safeguarding your health and well-being throughout your life.